1. Functions of flame arrestor
2. Concept of the flame arresters
3. Operating limits for a flame arrester
4. Guidelines in Selecting flame arrester
5. Flame Arrester construction type
6. Types of flame arresters
7. Approvals and Certifications
Flame Arrester (also spelled as Flame Arrestor) is a device fitted to the opening of an enclosure or to the connecting pipe work of a system of enclosures and whose intended function is to allow flow but to prevent transmission of a flame.
According to the Oxford English Dictionary there is no ‘correct’ spelling as both versions are valid. Within the deflagration and detonation research and manufacturing community the spelling ‘arrester‘ is more prevalent, although according to Google the spelling ‘arrestor‘ is the more commonly used search term.
Functions of Flame Arrestor:
Protects systems for generating, storing, and transporting gases and liquids of every hazard category against dangers such as endurance burning, deflagration and detonation.
Basic fundamental concept of the flame arresters:
The basic fundamental combustion process that occurs is mainly Explosion, which is nothing but abrupt oxidation or decomposition process that increases the temperature and pressure or both simultaneously.
The explosion can be further categorized as:
1) Deflagration– An explosion that propagates at sub sonic velocity
Types of Deflagrations:
a) Atmospheric Deflagration- occurs in open Air without a noticeable increase in pressure.
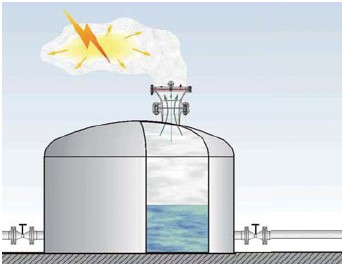
Atmospheric Deflagration
b) Pre-Volume Deflagration- occurs in a confined volume such as vessel, generally initiated by internal ignition source.
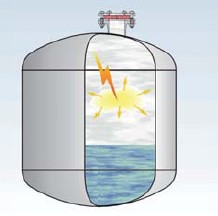
Pre-Volume Deflagration
c) In line Deflagration- accelerated propagation that takes place within the pipe along the axis of pipe at the flame propagation speed.
2) Stabilized Burning – even, steady burning of the flame at or close to the flame arrestor element
Types of Burning:
a) Short time burning – stabilized burning for the specific period
b) Endurance Burning- Stabilized burning for the unlimited period
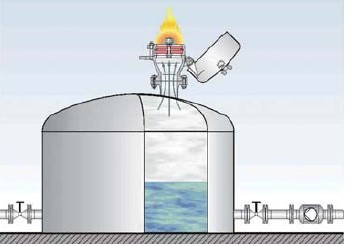
Stabilized Burning
3) Detonation– The explosion that takes place at supersonic velocity and is characterized by shock waves.
a) Stable Detonation- when it progresses through the confined system without the significant variation of velocity and pressure
b) Unstable detonation- is during the transition of the combustion process from deflagration to the stable detonation.
What are the operating limits for a flame arrester?
The main constraints applying to the use of flame arresters are:
- Operating temperature
- Operating pressure
- Run-up length
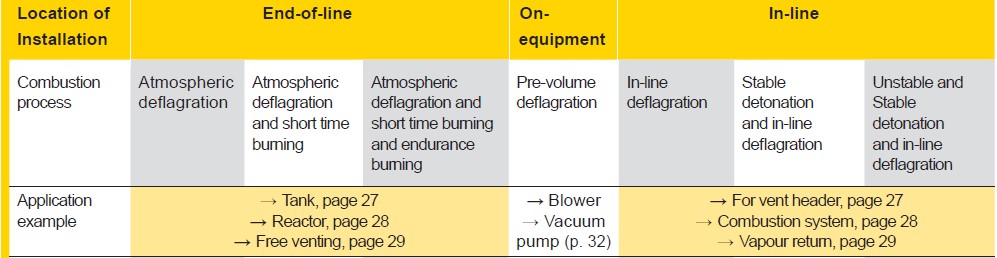
Operating limits of flame arrester
Explosion groups:
Explosion groups are important factor while selecting any flame arrester.
a) National Electric Code (NEC) (Group A, B, C and D)
b) International Electro technical Commission (IEC) classification (Groups I, IIA, IIB and IIC)
Guidelines in Selecting Flame Arrester
To help the manufacturers and users decide which flame arrester is the most suitable for their application, the following should be considered:
1) What is the service?
2) Analysis of Gaseous and Vapors
3) Moleculer weight and Density of Gas or vapor
4) Volumetric Flow rate
5) Temperature Range
6) Pressure Range
7) Allowable Pressure Drop
8) Type of Flame Arrester
9) Orientation of the flame arrester
10) Nominal Pipe size for connecting pipe work
11) Connection type
12) Housing Material
13) Element Materials
14) Construction
15) Documentation requirements
Flame Arrester Construction Type
To prevent the flame propagation, all flame arresters are equipped with “Element” or “Obstruction Component” that will disperse the flame front before it passes through the area that contains volatile gas/air mixture
Following types of Elements are available
- Wire Gauze
Wire Gauze
- Wire Gauze in packs

Wire Gauze in packs
- Perforated Plates

Flame Arrestor Element Perforated Plates
- Parallel Plates
Flame Arrestor Element Parallel Plates
- Sintered

Sintered
- Metal Foam
Metal Foam
- Crimped Metal
Crimped Metal
Material of Construction
a) Material of housing can be considered as ductile iron, carbon steel or stainless steel based on environmental conditions and cost economy.
b) Materials for valve seat can be selected of stainless steel.
c) Protective mesh screen shall be of stainless steel.
d) Material of construction for weather hood can be either carbon steel or stainless steel.
Types of Flame Arresters
The Flame Arresters are classified as below:
Depending upon the combustion process –
a) Endurance Burning
b) Deflagration
c) Detonation
Depending upon installation-
a) End of line -At the opening of the system part to atmosphere
b) In line-In the Pipe
c) In equipment–At the opening of equipment and (Pre-Volume) on to a connecting pipe
Approvals and Certifications
Flame arresters requires mainly following approvals
- FM approval
- ATEX
- GOST-R
- GL
- USCG
- IMO
- CSA