Mass Flowmeter
THERMAL MASS FLOWMETER
CORIOLIS MASS FLOWMETER
THERMAL MASS FLOWMETER
- Operates by monitoring the cooling effect of a gas stream as it passes over a heated transducer.
- Gas flow passes over two PT100 RTD transducers.
- The temperature transducer monitors the actual gas process temperature, whilst the self-heated transducer is maintained at a constant differential temperature by varying the current through it.
- The greater the mass flow passing over the heated transducer, the greater current required to keep a constant differential temperature.
- The measured heater current is therefore a measure of the gas mass flowrate.
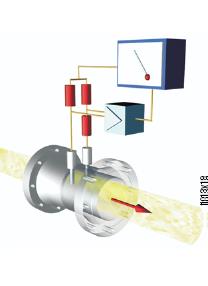
Thermal Mass Flowmeter
Features of Thermal Mass Flowmeter
- Design Pressure: 1200 PSIG
- Design Temperature: 176 Deg. C
- Sizes: 15 mm to 1000 mm
- Fluids : Clean gases
- Flow range: 0 – 2500 SCFM
- MOC: mostly in stainless steel/ glass, teflon, monel
- Accuracy is +1% to + 2% of flowrate
- Range ability is 10 : 1 to 100:1
- Upstream length/ Downstream straight length is 5/ 3
Advantages of Thermal Mass Flowmeter
- No temperature or pressure compensation required
- Linear output (as temperature differential is proportional to mass flow)
- Can be used on corrosive process streams if proper materials are specified
- DC voltage or 4 to 20 mA dc outputs available
Disadvantages of Thermal Mass Flowmeter
- Practical for gas flows only
- Subject to blockage by foreign particles or precipitated deposits due to small openings in flowmeter
- Power requirements excessive in larger pipe sizes
- Has to be taken out of process line for servicing
- Accurate field calibration is difficult
CORIOLIS MASS FLOWMETER
- When a moving mass is subjected to an oscillation perpendicular to its direction of movement, Coriolis forces occur depending on the mass flow.
- When the tube is moving upward during the first half of a cycle, the fluid flowing into the meter resists being forced up by pushing down on the tube.
- On the opposite side, the liquid flowing out of the meter resists having its vertical motion decreased by pushing up on the tube. This action causes the tube to twist.
- This twisting movement is sensed by a pick up and is directly related to mass flow rate
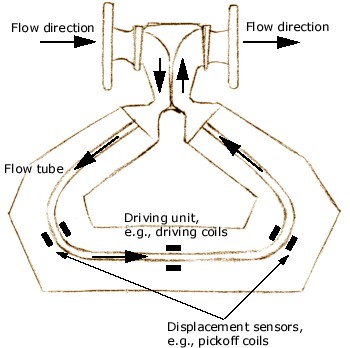
Coriolis Mass Flowmeter
Features of Coriolis Mass Flowmeter
- Design Pressure: 345 bar
- Design Temperature: 200 to 426 Deg. C
- Sizes: 1.5 mm to 150 mm
- Fluids/ Applications : Liquids (clean/ dirty/viscous/ slurries) clean /liquified gases
- Flow range: 0 – 25000 lb/m
- MOC: mostly in stainless steel, hastelloy/titanium
- Accuracy is + 0.15% to + 0.5% of flowrate
- Range ability is 20 : 1
- Bidirectional flow measurement
Advantages of Coriolis Flowmeter
- Capable of measuring difficult handling fluids
- Independent of density changes, flow profile and flow turbulence. Hence straight lengths are not required.
- No routine maintenance required since no moving parts
- High accuracy
Disadvantages of Coriolis Mass Flowmeter
- Not available for large pipes (upto 150 mm only)
- High flow velocities required for detection resulting in high pressure drop
- Expensive compared to other flowmeters
- Difficulty in measuring low pressure gases.