Drilling operation in offshore piping is a complex process with many challenges. Proper selection of each component is critical and various factors have to be considered such as the requirement, site conditions, design conditions, safety, cost, etc. The main components involved in the offshore drilling process are the drilling rig, the mud system, the blow-out preventer (BOP) etc.
THE MUD SYSTEM (BASICS):
- This mud scours the bottom of the hole to keep the bit cutters clean and keep a fresh rock surface for the bit to attack.
- Three Main Functions of the Mud are: (1) Cleans the bit, (2) Removes the Cuttings from the hole, (3) Keeps the hole from collapsing.
- Before re-entering the system again gas, sand and silt are removed from the drilling mud.
- The drilling mud should have sufficient density (mud weight) to prevent any gas, oil or saltwater from entering the well bore uncontrolled.
- The mud pumps and the engines that power them, represent the “heart” of the mud system just as the circulating mud is the lifeblood of the drilling operation.

Drilling mud system
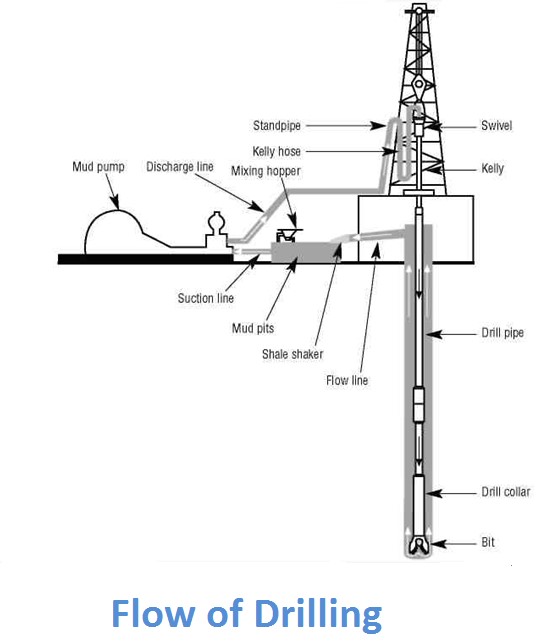
Flow of drilling
DRILLING RIG:
The main component of the jack-up rig which is critical for selection in a drilling operation is the drill string.
THE DRILL STRING
- The basic drill string is composed of drill bit, drill collars, Bottom Hole Assembly (BHA) and drill pipe.
- Each joint of drill pipe is around 30ft long.
- Each joint is between 2 3/8” to 6 5/8” in diameter depending on the location and the well type.
- The drill string is hollow for the continuous circulation of drilling mud.

Drill bit

Aligning of drill strings
BLOW OUT PREVENTORS (BOP):
- Sometimes formation fluids do enter the wellbore (the hole that is being drilled) under great pressure. When this happens, a well is said to “take a kick.” It is especially risky if the fluid is a gas or oil.
- To guard against the dangers of such events, rigs are usually equipped with a BOP.
- If a well takes a kick and the mud cannot stop or slowly release the pressure, the BOP is the last line of defense.
- If done correctly the gas is trapped in a bag type preventer and the mud and kick fluids special chemicals that are released into the hole to stop the gases/oils from reaching the Surface) are pumped out into a separate pit for disposal.

Blow out preventor (BOP)