Swing Check Valve:
Swing check valve is a non-return valve which operates by the swinging action of the disk. This valve is used for sizes 2” and above. There are two types of swing check valves available. They are the conventional swing check valves with flanged ends and the wafer type spring loaded check valves.
1. Conventional Swing check valve:
In this type of valves, the check mechanism is the disk which is hinged. The pressure of the fluid lifts the disk and allows the flow. The disk returns to the seat with its own weight. This allows the valve for mounting in horizontal as well as vertical position with upward fluid flow.
 Conventional Swing Check Valve |
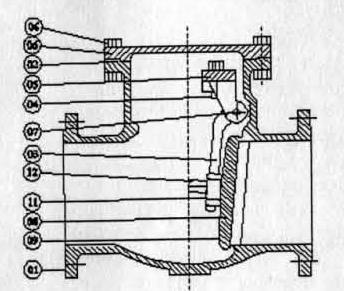 Conventional Swing Check Valve |
The main parts of the Swing check valve are –
- Body
- Cover
- Hinge
- Hinge Bracket
- Gasket
- Cover stud and nut
- Disc
- Seat Ring
- Hinge Pin
- Disc Pin
- Washer
The body will be cast with a tapered wedge seat and will be provided with renewable seat rings. The wall thickness and end to end/face to face dimensions of the body shall be as per the regulatory code to which it is designed. The end flanges shall be integrally cast or attached by welding. The flanged connection shall be to ASME B 16.5 or any other flange standard. The butt welding end connection shall be to ASME B 16.25.
The disk will be attached to the body through hinge and hinge pin and swings against the same controlling the flow. The disk material shall be of quality at least equal to that of the body.
The cover will be bolted on to the body. The bolted connection shall be raised face /tongue and groove/male and female/ring type joint depending on the pressure rating of the valve.
The gasket shall be selected to suit the type of connection. It can be corrugated or flat solid metal, corrugated or flat metal jacketed, asbestos filled, metal ring joint, spiral wound asbestos filled.
Flat ring compressed asbestos is used for low pressure application, Teflon or Teflon filled for corrosive applications. Normally high tensile bolts are used for cover bolting. In cast iron check valves low carbon bolts are used.
2. Wafer check valves:
The wafer check valve is a flangeless swing check valves. These are covered under the regulatory code API 594.
Compared to conventional check valves, these have less pressure drop across the valve in larger sizes, reduced water hammer and are compact.
There are two types of wafer check valve designs available.
- Single plate wafer check valve.
- Dual plate wafer check valve.
 Wafer check valve |
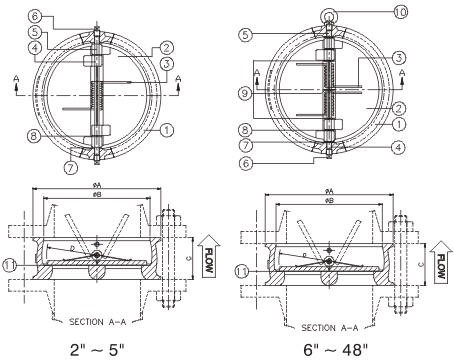 Wafer check valve |
The arrangement of single plate check valve is somewhat similar to the conventional swing check valve. Here a circular plate seated against the valve body seat by line back pressure or flow reversal acts as a valve closure. This is further aided by the provision of spring.
In dual plate check valves, there are two spring-loaded semi-circular plates. The plates are arranged in such a way that the spring force acts beyond the centre of area of each plate and the fluid force acts within the same. This fulcrum causes the heel to open first, preventing rubbing of the seal surface prior to normal opening.
The main parts of the wafer check valves are –
- Body
- Plate
- Spring
- Hinge Pin
- Stop Pin
- Plug
- Body Bearing
- Plate Bearing
- Spring Bearing
- Eye Bolt
The body is normally cast and is of any cast material. The sizes specified in API 594 are from
2” NB to 48” NB. Manufacturers have developed standards beyond these sizes as well.
The plates shall be made of material at least equal to that of the body.
The body and plate seating surface can be renewable or integral or with deposited metal. The seat surface could be stellited or can be of resilient material.
In these valves, the items specified under trim are the seating surfaces, springs, hinge and bearings. Table 4 of API – 594 gives trim numbers and the corresponding material of construction.